Pneumothorax symptoms are those caused by air accumulation in the lung. This condition, also known as lung collapse, requires medical intervention. It can arise due to various reasons. When the condition persists over a long period, its effects may vary, and the increasing air volume can also impact the heart.
What Is Pneumothorax? Pneumothorax Symptoms
Pneumothorax is the accumulation of air in the chest due to a rupture in the lung. This accumulated air prevents the lung from expanding properly, disrupting its function. Consequently, the individual finds it difficult to breathe. This condition, which is among the symptoms of pneumothorax, can start suddenly and is often accompanied by severe chest pain.
Pneumothorax is classified based on its type. You can review the table below for more information about these classifications.
| Type of Pneumothorax | Description |
|---|---|
| Simple Pneumothorax | A type where the air accumulation does not harm tissue and organ movements. |
| Open Pneumothorax | Requires immediate intervention. The lung may fully collapse. |
| Primary Pneumothorax | Develops spontaneously. Chronic conditions or health issues can be contributing factors. |
| Tension Pneumothorax | A serious condition requiring immediate attention. Symptoms include a drop in blood pressure and an increase in heart rate. |
How Does Pneumothorax Occur? What Are Its Symptoms?
Our lungs, which can be likened to a tree, transport air to their most distal points during respiration. In the alveoli, blood rich in carbon dioxide is oxygenated, supplying oxygen to the bloodstream. This respiration and oxygenation process occurs in a closed environment. If there is a rupture in the lung tissue, the incoming air becomes trapped between the lung and the chest wall. The symptoms of this condition include:
- Sudden and severe chest pain
- Difficulty breathing
- If the air leak is significant, sudden blood pressure drop
- Shock
- Increased heart rate
- Blue discoloration of the lips
- Cough
In some patients, there may be no symptoms. These are considered mild pneumothorax cases. However, if the lung fully collapses, the heart can become compressed and stop functioning. Immediate medical intervention is necessary in such cases.
Some of these symptoms may resemble those of lung cancer. Therefore, consulting a specialist is the first and most appropriate step when faced with such a situation. In our country, one prominent name in lung surgery is Professor Dr. Semih Halezeroğlu.
What Causes Pneumothorax?
 In addition to its symptoms, the causes of pneumothorax are often questioned. The reasons include:
In addition to its symptoms, the causes of pneumothorax are often questioned. The reasons include:
- Rupture of air sacs in the lung
- Lung infections causing tears in the lung
- Lung punctures due to trauma
- Use of tobacco products
- Genetic factors
- Respiratory failure
Among these, trauma is the most common cause. Additionally, the rupture of air sacs due to age or chronic illnesses often leads to lung collapse.
Who Is at Risk?
Pneumothorax arises as a result of the above-mentioned conditions. While some individuals recover without issues, others may experience serious complications. The risk group includes:
- Men aged 20-40 with a lean body structure who smoke
- Individuals with a history of lung disease
- Those with certain genetic disorders
- Individuals exposed to pressure changes
- Patients reliant on artificial ventilation
How Is Pneumothorax Diagnosed?
To diagnose pneumothorax, the patient’s complaints are first listened to. If the symptoms resemble those of pneumothorax, any prior lung-related issues are evaluated. A physical examination is also performed. During this examination, the loss or gradual reduction of breath sounds may indicate pneumothorax. In such cases, lung-related tests are necessary, including:
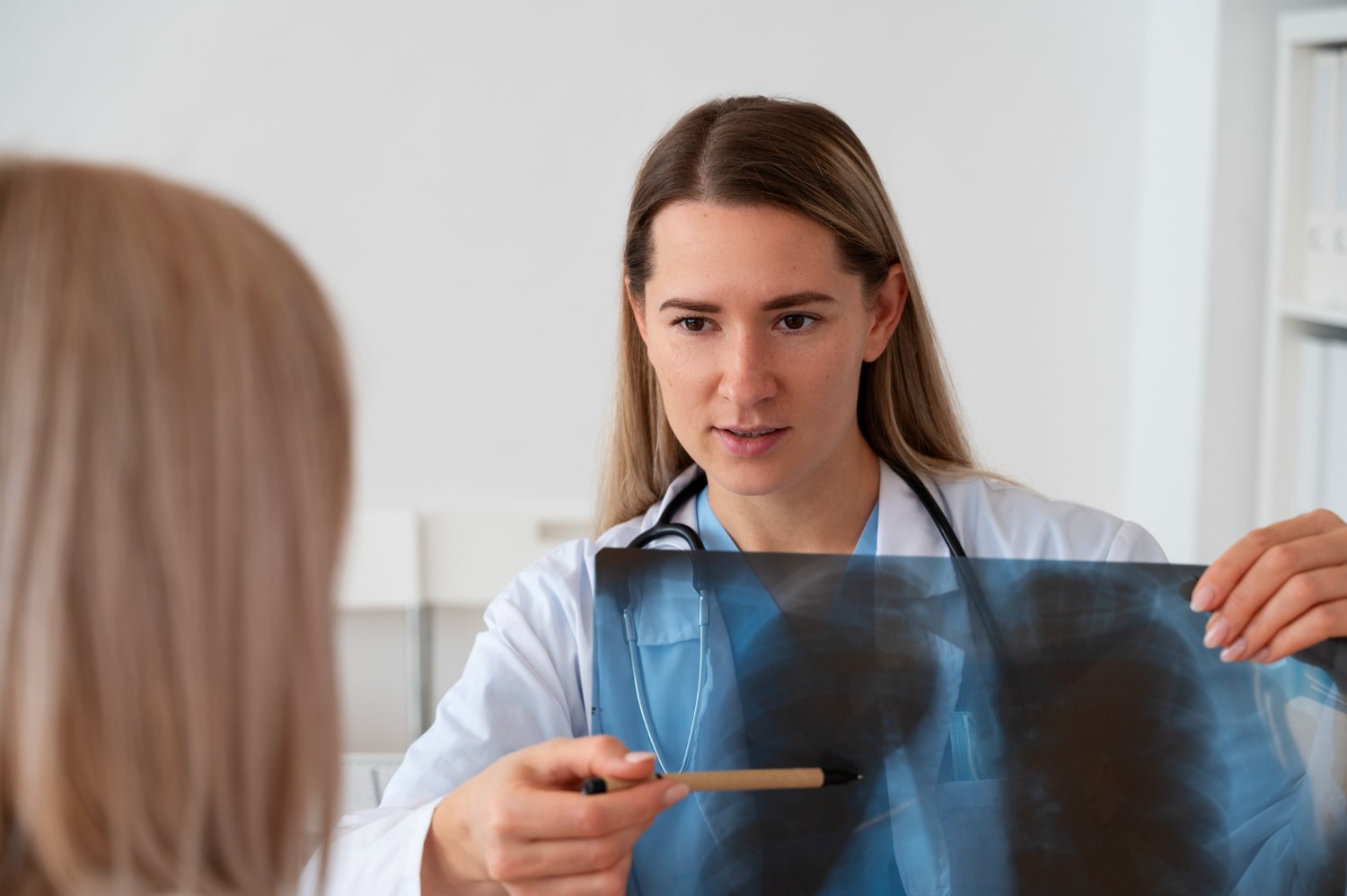
- Chest X-ray: The most commonly used test to diagnose pneumothorax symptoms. It determines whether there is air in the lungs and measures the volume of that air.
- Computed Tomography (CT): Provides a detailed image of the chest cavity, making it easier to diagnose underlying lung conditions.
- Arterial Blood Gas: This test checks oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other components in the blood to measure the level of acidity and assess the severity of respiratory issues.
- Pulse Oximetry: An electronic medical device that measures the approximate oxygen levels in red blood cells.
How Is Pneumothorax Treated?
Treatment methods vary based on the symptoms and diagnosis of pneumothorax. These include:
- Thoracostomy (Chest Tube Placement): Air can be evacuated by placing a tube in the chest cavity. This treatment suffices for most patients. The lung tear typically heals and closes within a few days.
- Oxygen Therapy: Suitable if the air leak causes a 10-15% lung collapse, clinical symptoms are absent or minimal, and it is the first occurrence of pneumothorax with no visible large air sacs on radiological tests.
- Underwater Drainage: Applied under local anesthesia to remove excess air when the air volume is high or the symptoms are bothersome.
- Closed Surgery: Used in cases of prolonged recovery or when large air sacs pose a risk of re-rupture. The damaged area is repaired, and air sacs are removed.
Post-Surgery Care
 After treating pneumothorax symptoms, paying attention to the following is crucial to ensure lasting recovery:
After treating pneumothorax symptoms, paying attention to the following is crucial to ensure lasting recovery:
- Avoid smoking and being in environments where others smoke.
- Take medications as prescribed.
- Engage in daily walks.
- Avoid straining activities such as heavy lifting or forceful straining.
- Consume plenty of fruits and vegetables.
- Attend follow-up appointments regularly.
Frequently Asked Questions
You can find the most frequently asked questions about pneumothorax symptoms below.
1 – How Long Does It Take for a Lung Collapse to Heal?
The recovery time depends on the type of condition. For example, in atelectasis, recovery is quick after a bronchoscopy procedure, with immediate symptom relief. In pneumothorax, patients are expected to recover completely within 2-3 days.
2 – What Is Closed Pneumothorax?
Closed pneumothorax refers to the entry of air into the pleural cavity from the lungs.
3 – Is There a Treatment for Pneumothorax?
Monitoring pneumothorax symptoms and performing the necessary procedures are crucial for treatment. With advancements in medical technology, the diagnosis and treatment of many conditions have become faster and easier.
4 – How Are Bronchi Cleared?
This procedure, known as bronchial lavage, involves the introduction of sterile saline into the airways. This allows sampling of cells in the airways.
5 – What Are the Symptoms of Lung Infection?
The most common type of lung infection is pneumonia. Persistent cough, bloody or yellow-green phlegm, are among the symptoms. Such infections must be treated.